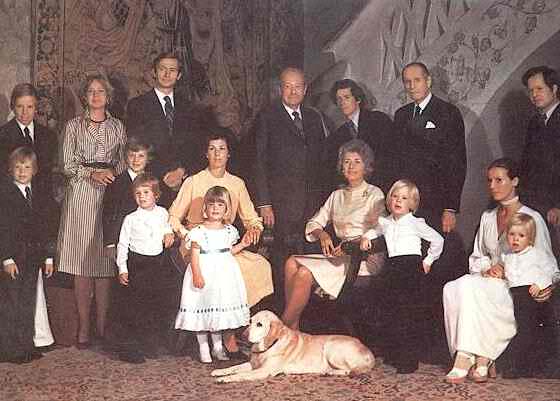

Figure 1.--This nportrait probably taken in the 1980s shows the family of Franz Joseph II with his sons and grandsons.


Figure 1.--This nportrait probably taken in the 1980s shows the family of Franz Joseph II with his sons and grandsons. |
Liechtenstein is the last independent remnant of the Holy Roman Empire. This small independent monarchy is bounded by Austria and Switzerland. The history of the principality dates from 1342 and acquired its present boundaries in 1712. At this time the House of Liechtenstein combined with Vaduz and Schelleberg which had previously been direct fiefdoms of the Holy Roman Empire. The line of succession has nor since been broken. Liechtenstein is a largely German speaking principality, but became independent of the German Confedration in 1868. The Principality then proceeded to demobilized its army and declare paermanent neutrality. A constutution providing for universal sufferage and proportianal representation was adopted in 1921.
Liechtenstein is a small independent principality bounded by Austria and Switzerland. Miunarins rise to naely 3,000 meters.
The economy of Liechtenstein has been largely agicultural. After World War II, began to shift from agroculture to industry. It has since become increasingly important as a financial centre and in 1998 had a very low unemployment rate. The European Union is concerned about problems associated with tax evasion. The country is united with Switzerland in a Customs Union and now has joined the European Union.
Liechtenstein is largely German speaking. Its peoples have many German and Swiss traditions, values, social courtesies and behaviour, but remain proud of their independent status.
Liechtenstein is the last independent remnant of the Holy Roman Empire. Liechtenstein was settled since the Neolithic age. The Romans conquered the region in 15 BC. The area was seized by a Germanic tribe, the Aleamanni in the 5thbcentury AD. During the Middle Ages it was ruled by different Houses. The history of the principality dates from 1342 when a Count Hartmann became ruler of the principality of Vaduz. The former County of Vaduz in 1396 obtained the Bestowal of Imperial Immediacy. Liechtenstein acquired its present boundaries in 1712. The House of Liechtenstein combined with Vaduz (1699) and Schelleberg (1712) which had previously been direct fiefdoms of the Holy Roman Empire. A few years later in 1719, Liechtenstein became an independent principality within the Holy Roman Empire. The line of succession has nor since been broken. French forces occupied Liechtenstein during the Napoleonic Wars. After the defeat of Napoleon, Liechtenstein regained its independence within the German Confederation in 1815 as part of the post-war peace settlement. Liechtenstein is a largely German speaking principality, but became independent of the German Conferation in 1868 after the Confederation as a result of the Austro-Prussian War. One of the Principality's first steps was to demobilized its 80-man army and declare permanent neutrality. Liechtenstein in 1919 entrusted its external relations to neutral Switzerland. A constutution providing for universal sufferage and proportianal representation was adopted in 1921. Liechtenstein neutrality was respected by the Germans during World War I and II. Russia in 1996 returned the Liechtenstein family's archives, ending a long-running dispute between the two countries.
Aloysius II was born in 1796. His father was John I of, Prince of Liechtenstein (1760- ). His mother was Josepha von Fürstenberg-Weitra (1776- ). He married Frances Kinsky (1831- ). They had seven children. Aloysius died in 1858. John and Framces succeeded him, but when both died childless, the crown passed to Franz Josef II, the grandson of Aloysius' third daughter Henrietta (1843- ).
John II was born in 1840. His father was Aloysius II (1796- ). His mother was of Frances Kinsky (1813- ). He acceded to the throne in 1858 upon the death of hos father. He ruled over 60 years, guiding Liechtenstein through both the Austro-Prussian and Franco-Prussian Wars ansd keeping the principalitybout of the new German Empire in 1871. The Prince signed the first Constitution in 1862. The members of the Diet were chosen by electors. Hecalso promulgated the more democratic constitution of 1921 which gave full political responsibility to the people of Liechtenstein. John II died in 1929 without marrying and had no children.
Francis I was born in 1853. His father was Aloysius II (1796- ). His mother was of Frances Kinsky (1813- ). He inherited the throne in 1929 upon the death of his older brother John II. Francius also did not marry and had no children.
Fran Joseph was born in 1906. His father was Prince Aloys (1869- ), a grandson of Aloysius II. His mother was Elisabeth Amalia Habsburg-Lotharingen (1878- ). Prince Franz Joseph II ruled Liechtenstein for 51 years. He in 1938 was the first Prince ever to take up residence in the castle of Vaduz. Franz Joseph married Georgina of Wilczek in 1943 during World War II. They had five children: John III Adam (1945- ), Philip Erasmus (1946- ), Nicholas (1947- ), Nora (1950- ), and Franz Joseph of Wenceslas (1962- ). Franz Joseph II died in 1989 and was succeeded by his eldest son John III Adam.
Franz Joseph II von Liechtenstein was in 1984 succeeded by his oldest son Hans Adam, who in 1989 took the name Hans Adam II. He married Mary Aglae Kinsky in 1967. They had four children: Alois (1968- ), Maximilian (1969- ), Constantine (1972- ), and Tatiana (1973- ). Prince Hans Adam was granted all the Regency's executive powers in 1984 and rose to the throne upon his father's death in 1989. Hans Adam in late 1993 revised the Hausgesetz (the 'house code' of the ruling family), including the right for the population constitutionally to depose him or even abolish the monarchy altogether if they so wished.
Pince Alois was born in 1968. We know nothing of his childhood at this time. He married to Princess Sophie of Bavaria (1967- ). Suggestions that Prince Hans Adam II would step down in favour of his son, Crown Prince Alois, have not so far occurred. Prince Alois married Sophie Wittelsbach in 1993. Prince Hans Adam II formally handed over day to day governing power to his Prince Alois (2004). The entire population of the principality was then invited to a garden party. Prince Adam continued, however to retain overall authority.
Navigate the Boys' Historical Clothing Web Site royal pages:
[Main Germann States Royal pages]
[Main royal pages]
[Austria]
[Bavaria]
[Belgium]
[Denmark]
[France]
[German Empire]
[German states]
[Italy]
[Luxenburg]
[Monaco]
[Netherlands]
[Norway]
[Romania]
[Russia]
[Spain]
[United Kingdom]
